燙傷的醫療處置
燙傷的分類
Scald burn
•Most common in children, also in elderly patient
•Depend onwater temperature, skin thickness, and the duration of contact
(60 degree 3 seconds = 69 degree 1 s, deep dermal burn)
•Grease and hot oil
Flash or flame burn
•Prolonged exposure to intense heat
•Often associated with inhalation injury and other concomitant trauma
Contact burn
•Extremely hot or abnormally long
•Usually deep thermal or full thickness
Electrical burn
•High voltage (>1000 V)
•Extensive skin injury with necrosis at the contact point and deeper structures
•The resistance of tissue gradually from **nerves to vessels, muscle, skin, tendons, fat and bone
•Multi-organ injury
•Like crush injury, traumatic injury
Low voltage (<1000 V)
Flash burn (no current flow through the body)
Lightning
•Point of electrical burns
•Entry and exit point
•Compartment syndrome need fasciotomy
•Myonecrosis, with severe myoglobinemia\(massive muscular destruction\) can lead to acute renal failure
•Cardiac dysfunction: atrial fibrillation or supraventricular arrhythmias
Chemical burn
•Frostbite, cold injury 凍傷
燙傷初步評估
Airway and cervical spin control
•Nasal endotracheal tube, tracheostomy
•Upper airway obstruction can develop quickly
Breathing
Circulation
•Good iv access and give fluids
Neurological disability
Exposure with environmental control
Fluid resuscitation
•Assess burn size and depth
•Good iv access and give fluid
•Analgesics
•Foley, blood test, CXR, EKG, GAS,COHb
轉診至燙傷中心之適應症

燙傷的深度
Function of skin
•Thermal regulation and prevention of fluid loss
•Hermetic barrier against infection
•Sensory receptors
First degree, epidermal burn
•Second degree
•Superficial partial thickness burn
Deep partial thickness burn
Third degree, full thickness burn
Forth degree
Local and systemic response
•Zone of coagulation, zone of stasis \(decrease tissue perfusion\)
•Release of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators if over 30% TBSA
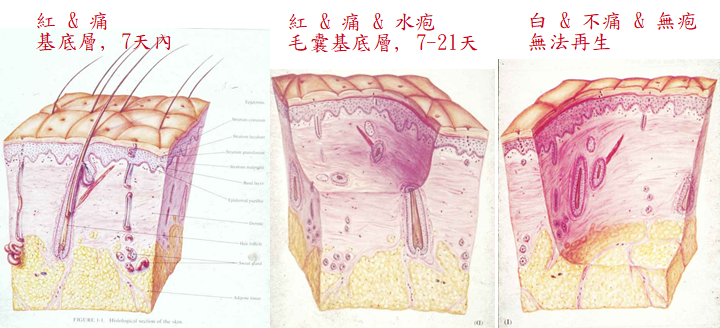
Epidermal Burn (1st Degree)
Red and quite painful
No blister
Subside over 2-3 days
Day 4: injured epithelium peels脫皮
Day 7: healing complete
Treatment
•Supportive care
•Pain control
•Cold compression
•Topical emollients

Superficial Partial Thickness Burn
2nd degree burn 淺二度燙傷 : Blanching sign
Epidermis and superficial dermis, blistering is common水泡
Healing is expected within 14 days
殘留較多皮膚附屬器:汗腺,毛囊,皮脂腺
Most superficial facial burns heal well with watchful neglect. Progression to a deeper burn
•Wound dries out
•Infection
•Patient becomes systemically unwell or hypotensive
Treatment
•Preventing wound progression by the use of antimicrobial creams and occlusive dressings
Deep Partial Thickness Burn
深二度燙傷
Most difficult to assess and treat
Wounds usually mixed superficial and deep
•Re-examination in 48 hours
•Less skin appendages density
•The burn takes longer to heal, the scarring is more severe and associated with contraction
Spontaneous healing: 3-9 weeks
Treatment
•In extensive or in functional or cosmetically sensitive areas: better excision and skin graft
•Avoid infection
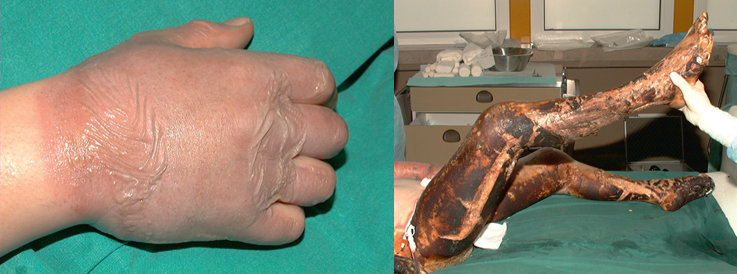
Full Thickness Burn(3 rd Degree)
Epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous structure
White or charred
Burn eschar
Only healing by edge and contracture
Some even involved muscle, tendon, ligament or bone (4th degree)
燒傷深度的評估
Degree of burn injury :紅-->水疱-->白(毛囊修復)
•First degree : epidermis
•Second degree : epidermis + dermis(partial)
•Third degree : entire dermis + all deep epidermal elements
Scald; flame; inhalation; electrical; chemical; contact
溫度及時間對細胞之影響
1.45℃,1小時:細胞膜破壞、細胞死亡
2.可逆性(急速降溫)
Immersion time to producefull-thickness burns
Time Temperature (°F)
1 second 158 (70℃)
2 seconds 150 (65℃)
10 seconds 140 (60℃)
30 seconds 130 (55℃)
1 minute 127 (53℃)
10 minutes 120 (48℃)
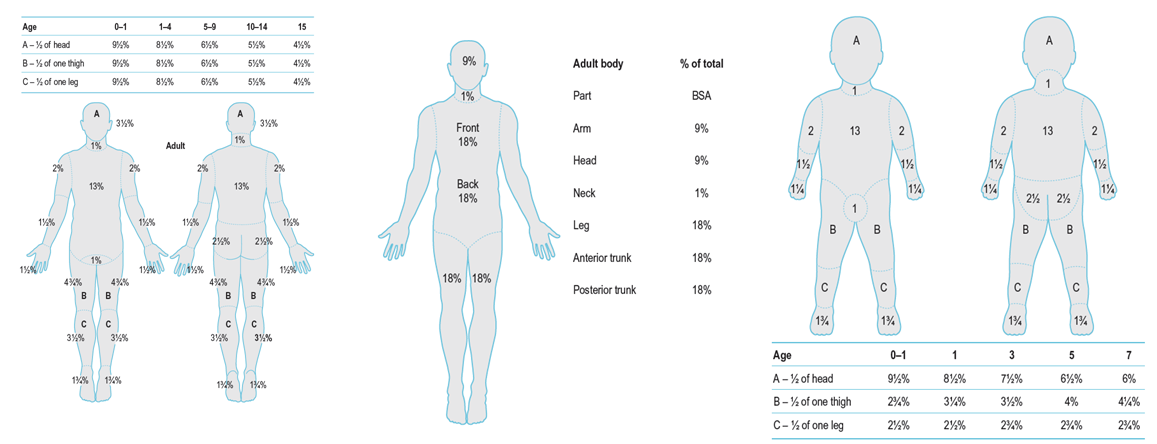
燙傷面積估算
Units: total body surface area, %TBSA
Over 2nd degree burn
Adults, rule of nine
Inhalation Injury吸入性灼傷
Signs of inhalation injury
•History of flame burns or 密閉空間燃燒
•Full thickness or deep thermal burns to face, neck or upper thorax
•Singed nasal hair 燒焦的鼻毛
•Carbonaceous sputum or carbon particles in oropharynx
High mortality and morbidity
Signs of COHb
Indication of intubation
•Erythema or swelling of oropharynx on direct visualization 口咽紅腫
•Change in voice, with hoarseness or harsh cough 聲音沙啞
•Stridor, tachypnea, or dyspnea 喘
•Carbonaceous particles staining a patient’s face after a burn in an enclosed space 火場內灼傷,臉部有黑炭
傷口清洗及包紮
Hydrotherapy
Topical ointment
•Silver sulfadiazine
•Most common
•Intermediate wound penetration and a good antibacterial spectrum
•Change bid
•Mafenide acetate
•Bacitracin
Wound dressings
•Biological
•Human cadaveric skin, allograft
•Physiological
Resuscitation from burn shock
Crystalloid solution : (first 24 hours)
a.Lactated Ringer’s solution(Na : 130mEq/L)
Colloid solution :
a. Fresh frozen plasma 0.5-1 ml/kg/%
b. Human serum albumin (25% 50 ml: 12.5gm) (1 : 5稀釋)
Parkland formula
前24小時:4 cc. LRxburn (%)xBW (kg)
•前8小時: ½;後16小時: ½
次24小時: 5 % Dextrose in water
•(1/2 first day requirement)
•Colloid : 0.5-1.0 cc/kg/% burn
•Albumin: 12.5 gm/50cc (over 2-4 hours)
大面積燙傷照顧重點
Initiation of fluid resuscitation
•Adults: >20% TBSA
•Child: infants with burns of ≥10% TBSA and in older children with burns ≥15% TBSA
•Lactated Ringer’s solution
•Urine output (Foley catheter)
•Adult: 0.5–1.0 mL/kg
•Child: 1.0 -2.0 mL/Kg
Crystalloid in first 24 hours, start colloid (albumin or FFP) after 24 hours
Central venous pressure line
Nasogastric (NG) tube should be placed ≥20% TBSA
•Prevent gastric distention and associated emesis
•Enteral nutrition
大面積燙傷-輸液治療 燒傷輸液急救之監測
燒傷輸液急救之監測
1.Urine output : 0.5-1 cc/kg/hr
-- Electric injury: 2 cc/kg/hr(myoglobin)
-- Child : > 1 cc/kg/hr
2.Hemoglobin(Hgb) : 12-14 mg/dl
Blood pressure: arterial line
CVP: Not a reliable indicator of the adequacy of resuscitation
Swan-GanzPulmonary artery catheter: Pulmonary wedge pressure = Left arterial pressure (10-15 cm H2O)
急性燙傷手術

燙傷後身體代謝變化
- Nutritional therapy play a key role of wound healing
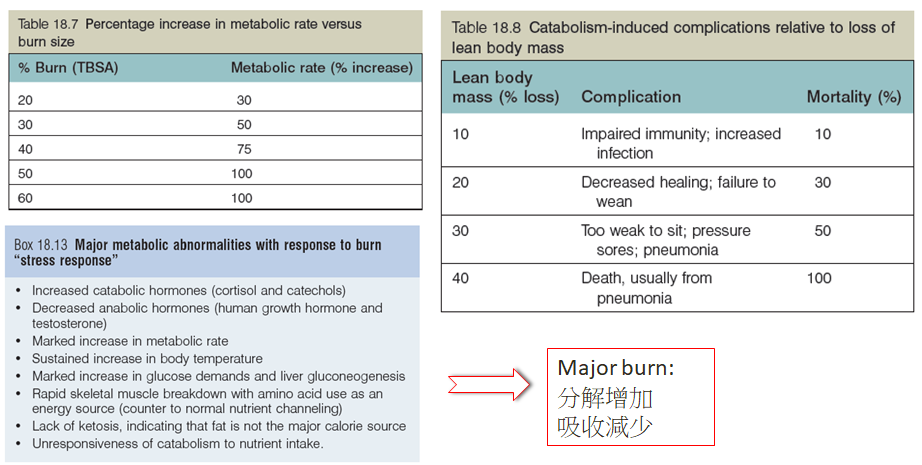
營養治療
Major burn (> 20%)
•Oral intake is not enough
•Enteral nutrition through nasogastric or nasoduodenal transpyloric tubes \(tube feeding\)
•The rigorous schedule of dressing changes, operations, and rehabilitation sessions interferes with meals
•High-dose analgesics
•Early enteral nutrition can relieve gastrointestinal damage, and maintain the integrity of intestinal mucosa after
severe burn
Nutrition formula
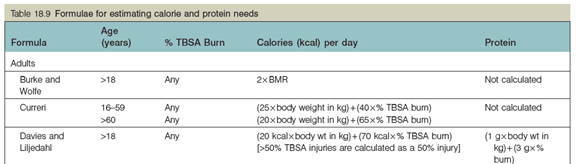
燒傷之營養評估與補充
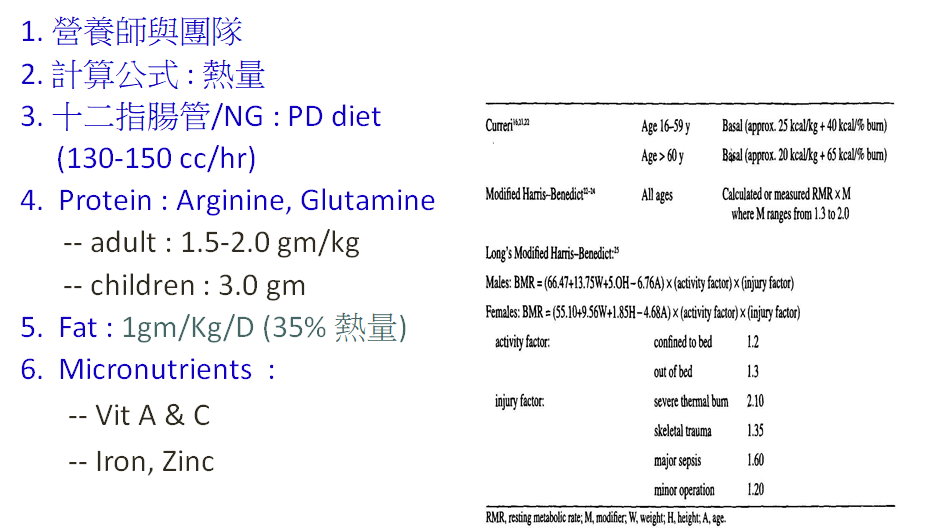
燒傷傷口的治療原則
I degree : ice compression, oil, pain control
II degree :
•移除抽吸水疱
•生物敷料(阻隔,止痛,抗菌,促進癒合)
III degree :
•Escharotomy
•Allograft, xenograft
•Autograft(split-thickness skin graft :STSG)
Facial 2nd(II) degree burn :
•Open care : antibiotic ointment(Biomycin)
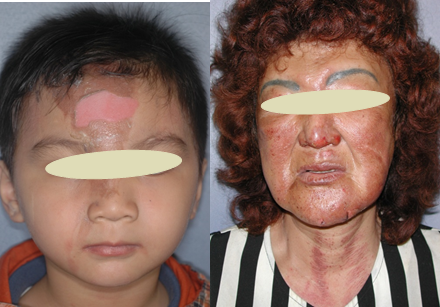
- Biological dressing : Aquacel (Ag)
•Hydrocolloid
•Ag :抑制殺死嗜氧,厭氧,黴菌
 燒傷傷口的治療原則
燒傷傷口的治療原則
Burn wound management :
•7天; 14天; > 21天
•Porcine skin graft
•Cadaveric skin graft
•Biological dressing
•Topical antibiotic cream
•Systemic antibiotics ?
•Skin graft : STSG
•FTSG : joint (prevent scar)
Blisters & vesicles :
•弄破水疱
Topical antibiotic cream
最常用;水溶性;濃度1%, 12-24小時換一次•
效用: G(+), G(-); Candida albicans, herpes viruses
Minimal pain, non-staining, thin pseudoeschar
SE : systemic absorption (rare toxic);leukopenia(after 2-3 days)-->DC ifWBC <2,000
燒燙傷最新的治療原則
Aggressive resuscitation : start at ER
> 25 % TBSA : intubation
Escharotomy
Early debridement
Early temporary dressing coverage : CSG
Early skin graft
Growth factors & skin substitutes

Start at ER
A-->B-->C
40% TBSA : 500 ml/hr
60% TBSA : 1000 ml/hr
依照輸液流程表
Albumin replacement : 8小時

Early debridement & cadaveric skin graft coverage
Early skin graft : Scalp skin, Mesh, Meek

PDGF, EGF, KGF
Glue & platelet gel
Cultured epidermis
Integra
Artificial skin
復健治療
Restoration to health and work capacity
Aim
•Preventing scarring
•Recover confidence in their ability to work and enjoy life
Regular physiotherapy several times per day
Starting physiotherapy from 1st day of patient’s admission and as early as the 3rd day of grafting
Early chest physiotherapy to prevent remove secretions and prevent atelectasis
Exercise and stretching therapy to prevent joint contracture
Ankle pump exercise several times per day
Prevention of muscular atrophy with passive and active (with and without load) exercises ± electrical stimulation
Ambulation as soon as possible
Education of the patient’s family to help the patient and the burn care professionals
Consideration and prevention of secondary complications (e.g., frozen shoulder, scoliosis, etc.)
Use of splinting and modalities (e.g., ultrasound) based on patient’s need to protecting the skin grafts and preventing the burn scar
Encourage activities of daily living with emphasis on fine movements and joint mobilization.
Silicon and pressure garment therapy
Complications
Skin graft loss
Infected wound
•Should be suspected if the wound becomes increasingly uncomfortable, painful, or smelly; if cellulitis or fever
•Regular and repeated wound culture
Compartment syndrome 腔室症候群
•Elevated pressure in fascia, extensive edema
•Risk: circumferential full-thickness burns (neck, thorax, abdomen, extremities)環狀三度灼傷
•Treatment:escharotomies, fasciotomies, or both